Table of Contents
Your personal favorite and efficient LED lights, be it simple light bulbs, light bars, or ceiling lights, have an enemy hindering their performance, i.e., Heat. Yes, you heard it right. These light-emitting diodes use the semiconductor to brighten up any spot when in contact with a power source. However, these lights produce less heat than incandescent lights, but the small amount they do simply impacts their performance. Even if these lighting fixtures are changing the lighting industry from common households to commercial places, the heat is to bring mechanical failure. So, in this article guide, we will answer do LED lights get hot, discuss some of the factors causing heat and how to manage it efficiently.
Understanding LED and Heat Technology
We’ll deeply delve into the technology LED lights use and how they generate heat.
How do LED Lights Work?
Before finding the answer to whether LED light bulbs get hot, first, there is a need to uncover the workings of these light bulbs.
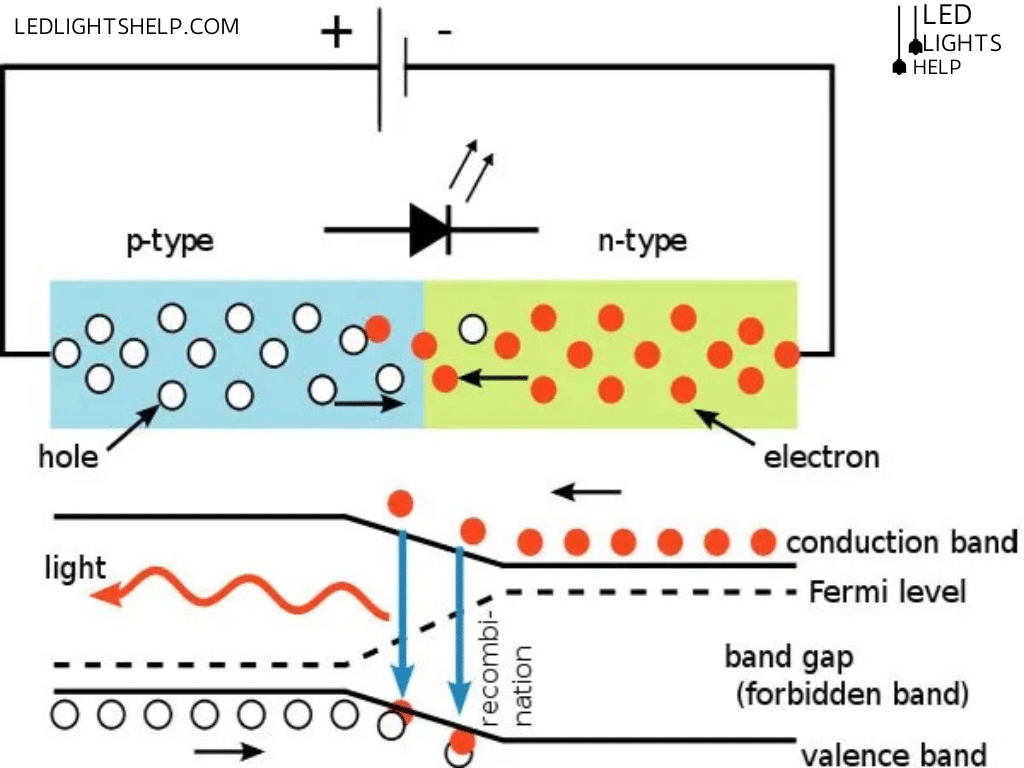
Semiconductor devices called light-emitting diodes, or LEDs, produce light when an electric current flows through them. LEDs work on the idea of electroluminescence, as opposed to traditional incandescent bulbs, which generate light by heating a filament. A p-n junction is produced in an LED light by doping a semiconductor material with impurities. Electrons and electron holes rejoin at the junction when a voltage is placed across it, releasing energy in the form of photons. In contrast to incandescent bulbs, which lose a large amount of energy as heat, this technique generates light and is far more efficient.
You can check out the details of LED and heat technology in this article.
Production of Heat in LED Light Bulbs
We should know that LED strip lights or bulbs produce heat even though they are highly efficient. The energy conversion mechanism occurring within the semiconductor material is the main source of this heat. Some energy is transformed into heat instead of light when electrons and electron holes recombine to produce light. Heat generation is also a result of resistive losses in the semiconductor material and other parts of the LED package. Even though LEDs generate less heat than traditional types of bulbs, effective heat management is still necessary to guarantee longevity and peak performance.
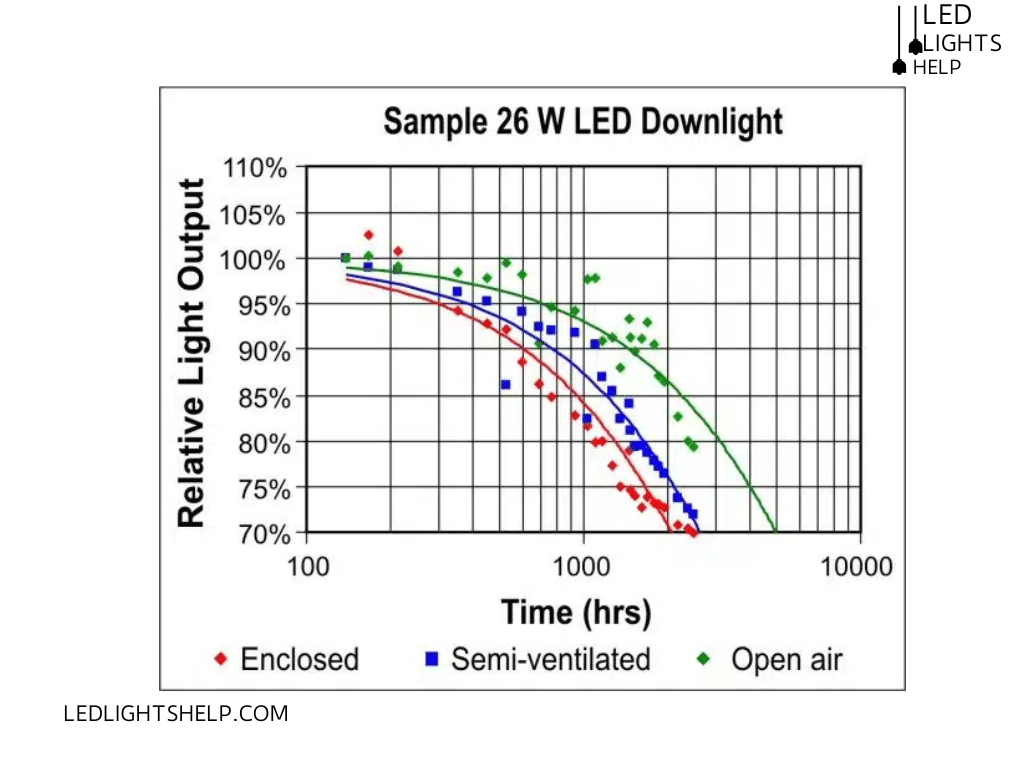
Elements That Affect LED Temperature
Everyone praises the energy efficiency of LED light bulbs; these lights get hot. Although the amount of heat and damage caused by it varies, so if you are thinking about LED lights getting hot enough to start a fire, there is a need to delve deep into it. We’ll go through several factors that affect the temperature of these bulbs, and light output brings the heat.
Drive Current
The LED’s temperature is directly impacted by the drive current or the amount of electrical current that is applied to it. Elevated heat generation is a consequence of enhanced electron mobility in the semiconductor material caused by larger driving currents. LED manufacturers offer the highest drive currents, which are advised to avoid overheating. Heat dissipation or generation can be decreased by running LEDs at lower currents, although light output can also be reduced. So, it is very obvious that LED lights, be they strips, bars, Christmas, or bulbs, get hot.
Ambient Temperature
LED performance and heat are highly influenced by ambient temperature, or the ambient temperature. High ambient temperatures force LEDs to work at greater temperatures because they limit the efficiency of heat dissipation systems. Reduced effectiveness, color alterations, and shortened longevity are possible outcomes of this. When developing LED lighting systems, ambient temperature must be taken into account. Proper airflow and cooling must also be maintained to maintain ideal working conditions. However, if you have another question popping up in your mind, how hot do LED light bulbs get? It simply varies depending on which factor is causing it to get hot.
Enclosure Design
The heat management of the enclosure or LED fixture is greatly influenced by its design. LED temperatures can rise in enclosures with inadequate heat sinks or inadequate ventilation, which traps heat. In order to promote heat dissipation, proper design includes elements such as heat decreases, ventilation openings, and heat-conductive materials. Heat sinks are frequently utilized to improve the heat transfer surface area, and ventilation apertures facilitate the removal of heat from the LED components by airflow. Optimizing LED performance and reducing heat buildup are two benefits of good enclosure design.
Heat Control in LED Lights
Thermal management strategies are designed to keep LED components cool and at the ideal operating temperature. To increase heat transfer and boost thermal performance, thermal pads, heat sinks, and heat-conductive materials are frequently employed. Heat sinks are intended to absorb and disperse heat away from the LED.
They are usually made of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum. By filling up spaces and air cavities, thermal pads positioned between the LED and the heat sink ensure effective heat transfer. Optimizing LED efficiency, longevity, and dependability requires proper thermal management. Once you have figured out how hot do led lights or Christmas get, you have to effectively manage them.
Do LED Lights Get Hot Enough to Melt Plastic?
This is a common question many people ask, and the answer is no. LED lights don’t get that hot to melt anything.

Controlling the Heat Emitted by LED Lighting
There are several proven strategies to control heat dissipation generated through LED lights.
Heat Sinks
The purpose of passive cooling devices, known as heat sinks, is to divert heat away from LED components. They are made up of metal plates or fins that increase the heat transfer surface area. In order to effectively absorb and dissipate heat, heat sinks are usually constructed of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum. Heat sinks help maintain ideal LED temperatures and protect against overheating by improving heat dissipation.
Thermal Pads can Control Heat from LED Lights
To enhance thermal conductivity and guarantee efficient heat transfer, thermal pads are soft, foldable pads arranged in between the LED and the heat sink. By closing up spaces and air gaps between the LED and the heat sink, they improve heat dissipation and remove thermal barriers. Thermal pads come in a variety of thicknesses and thermal conductivities to accommodate a range of applications. They are often composed of silicone or other thermally conductive materials.
Sufficient Airflow
To prevent heat from escaping into the surrounding area, there must be enough ventilation around the LED fixture. An enclosure’s heat buildup can be avoided, and LEDs’ ideal temperature settings can be maintained with proper airflow. Depending on the needs of the application, forced air cooling systems or natural convection can be used to produce ventilation. Performance and dependability can be maximized by efficiently managing the heat emitted from LED lights.
Appropriate Fixture Design
Heat management features are included in well-designed fixtures to guarantee excellent thermal performance. To reduce heat buildup, this involves effective heat sinks, ventilation openings, and thermal insulation. To achieve optimal thermal management, fixture design should take into account elements including the surrounding environment, LED specifications, and heat dissipation needs. A well-designed fixture minimizes the chance of overheating and early failure while optimizing LED efficiency and lifespan.
Operating Conditions
Running LEDs at the recommended temperature range is essential for best results and longevity. Overheating the advised temperature ranges can cause color shifts, poorer efficiency, and shorter lifespans. Maintaining optimal LED performance involves keeping an eye on operational circumstances and applying appropriate thermal management approaches. This entails managing the ambient temperature, making sure there is enough ventilation, and efficiently dispersing heat by applying the proper heat management techniques.
You can also have a look at the differences between traditional lighting and LED lights in this article.
Conclusion
Summing up, the article covered details on the phenomenon of heat generated through LED lights. Several strategies to effectively manage the heat are also discussed. So, read our article and don’t worry about the heat.